How to Eat Edamame? Discover Its Health Benefits and Tasty Recipes
September 17, 2020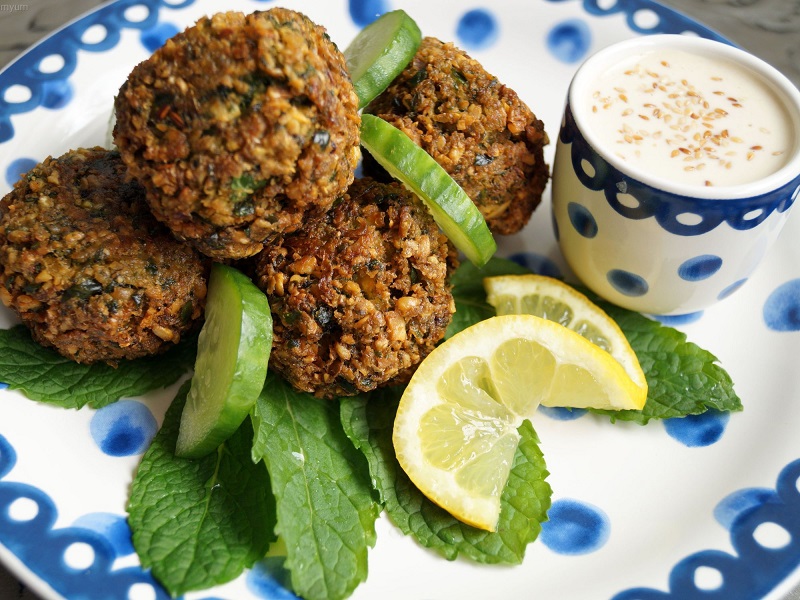
Chickpea meatballs and vegan vegetables, cold dish for the summer
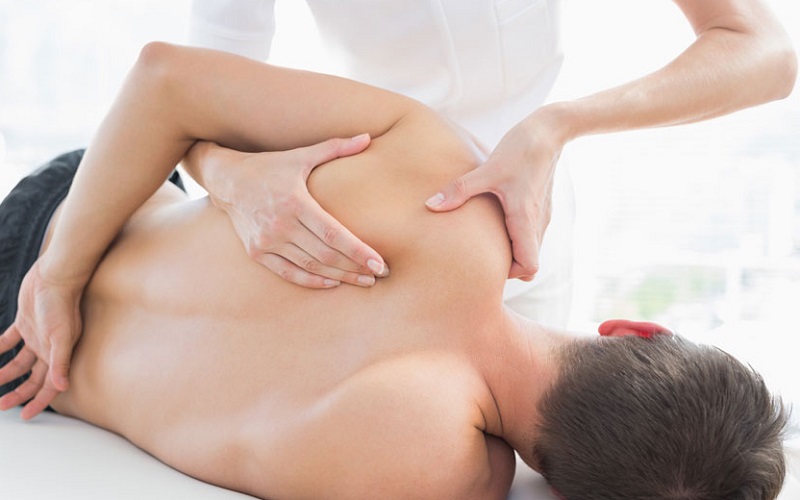
September 18, 2020Overcoming shoulder blade pain: exercises to recover better
The pain in the shoulder blade is a fairly common disorder, which can occur for reasons related to the bone and muscles that are grafted on it, or be caused by disorders affecting other organs.
The scapula is a flat, even bone (i.e. symmetrically present on both the right and left), triangular in shape and located at the dorsal surface of the thorax in the area between the base of the neck and the back. Its physiological function is to support the movement of the shoulder through the support it offers to the levator muscles of the scapula, rhomboid, triceps, trapezius, and deltoid.
Table of Contents
ToggleCauses of shoulder blade pain: the most common is muscle contracture
The most common cause of shoulder blade pain is muscle contracture, which affects the levator scapula muscle in particular. In these cases, the pain arises in the upper portion of the bone and spreads towards the nape of the neck, accompanied by stiffness, difficulty in moving the shoulder, and sometimes a muscle-tension headache.
Contracture can be triggered by incorrect or excessive exercise, poor posture, or spinal or shoulder abnormalities. The most involved alterations of the spine are hernias or disc protrusions, pathologies that involve compression of the nerve radicles of the fibers that innervate the upper limb. In these cases, the pain can radiate to the arm.
The shoulder pathologies most commonly responsible for shoulder blade pain are Impingement Syndrome (which involves rubbing between the humerus and the shoulder blade as the arm moves upward, generating pain in the shoulder blade) and inflammation of the cuff of the shoulder blades. rotators (the complex of the four muscles and respective tendons that contributes to the movement of the shoulder).
The traumatic diseases may be the cause of this type of pain, even though incidents such as the fracture of the scapula are relatively rare. Shoulder injuries are more common.
Even assuming an incorrect posture can cause pain in the shoulder blade. This problem is particularly common in those who spend a lot of time in front of the computer in positions that are detrimental to the balance of the musculoskeletal system. In this case, the affected shoulder blade is the one corresponding to the hand that moves the mouse.
Psychological conditions of fragility or exposure to intense stress can trigger phenomena of muscle stiffening that degenerate into contractures.
Other contingent situations such as holding a child for many hours a day or carrying backpacks containing heavy books can cause this disorder.
The infection herpes zoster (also known as shingles ), which mainly affects the elderly, can cause burning pain in the upper back, accompanied by paresthesia (tingling) and the appearance of a rash consists of clusters vesicles following the course of the nerve.
Pain in the shoulder blade can be a sign of pathologies affecting other anatomical areas, such as the lung (pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, tumor) or the heart (myocardial infarction). Also, if the shoulder blade hurts from coughing or breathing deeply, the problem usually involves the intercostal muscles.
How to cure shoulder blade pain
Before proceeding with shoulder blade pain therapy, a diagnosis should be established and the responsible factor removed, if possible.
In any case, it is important to avoid carrying heavy bags and backpacks, to which draggable trolleys should be preferred. It may also be useful to replace the mattress if it is too hard or too soft and choose a model on the advice of your doctor or physiotherapist based on your problem.
To counteract the risk of shoulder blade pain from long stays at the PC, it is good to observe some rules. Like placing the monitor below the horizontal visual axis and at least once the size of your arm away from you. Furthermore, the keyboard and mouse should be in line with the elbows: it is advisable to use a support for the elbows if these protrude from the support surface. A footrest could be helpful in reducing strain on the back. It is also important to keep the back well supported against the backrest.
Mild shoulder blade pain can be treated by applying local pain relievers (formulated in cream or patches) or heat and cold therapy pads. In case of intense pain, the doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatories to be taken by mouth, muscle relaxants, or steroid infiltrations.
For the purpose of rehabilitation, it may be useful to undergo targeted and personalized physiotherapy cycles.
Shoulder blade pain some exercises to recover better
In the case of mild contractures, it is possible to accelerate recovery by regularly carrying out exercises aimed at rehabilitation, also with a view to preventing relapse.
Exercise 1: Stretch the muscles
Here is another exercise to stretch the muscles and unload the shoulder blades. Raise the right arm and fold the forearm down so that the hand touches the left hand passed behind the back. Open the chest by inhaling deeply and stretching the pectoral muscles. This exercise must be performed 5 times on each side.
Exercise 2: Loosen the shoulder blade muscles
To loosen the shoulder blade muscles, roll your shoulders back and forward, describing a letter C. Perform the exercise 10 times in each direction.
Exercise 3: Counteracting the effects of poor posture
To counter the effects of poor posture, this simple exercise can be helpful. Sitting on the ground with your back straight and legs crossed, move your chin back while keeping your head aligned with your spine. Then stretch your head upward, as if a hook is pulling it in that direction. This exercise within everyone’s reach helps to unload the shoulder blade area.